LogicMonitor - Network Topology
Role: Product Manager
Situation
LogicMonitor develops infrastructure monitoring tools tailored for enterprise IT and managed service providers. Network topology within LogicMonitor allows for the dynamic discovery and visual representation of network resources (such as links, nodes, etc.) and their connections. Key use cases for understanding network topology include:
- Issue resolution
- Capacity planning
- Performance optimization
- Network design and configuration
- Documentation
The topology map includes resource alerts, making issue resolution the primary focus for this feature.
Task
LogicMonitor’s objective is to help customers reduce Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR), decrease downtime, and proactively mitigate network-related issues. For network topology, this specifically means enhancing the issue resolution process. Customer research identified a major barrier to this goal: the “Storm of Alerts” challenge.
In complex network topologies, a single incident can trigger hundreds of alerts, even though only a fraction of them require action. For example, a minor network disruption may generate over 500 alerts, though only 10-20 may be necessary to resolve the issue. This alert storm complicates management, increases MTTR, and often overwhelms IT operations teams.
Action
To address this, we focused on automating Root Cause Analysis (RCA). The team determined that machine learning could provide a scalable solution for RCA by utilizing topology relationships to establish dependencies among resources.
When a monitored resource becomes unreachable, these dependencies are analyzed to identify the root cause and affected resources. By isolating the root cause and sending alerts only for impacted dependent resources, we prevent typical alert storms and streamline notifications. This RCA-driven approach significantly reduced alert noise, allowing IT operations engineers to focus on actionable alerts, thus reducing MTTR and minimizing downtime.
Result
We implemented Dependent Alert Mapping, which leverages automatically discovered relationships between resources to detect the root cause of alerts and notify users of the original incident. When a critical device goes down, impacting connectivity for downstream devices, Dependent Alert Mapping disables notifications for those downstream resources, ensuring engineers receive only the most relevant alerts.
Metrics Achieved:
- MTTR: Customers utilizing Dependent Alert Mapping saw a 20-40% reduction in MTTR, contributing to LogicMonitor’s goal of a 15% MTTR reduction across all users.
- Alert Volume: The feature suppressed 50-90% of non-critical alerts for customers, depending on the complexity of their infrastructure and incident management maturity.
Appendix
Research Methodology
User Experience
Topology view highlights the impacted parent device and dependent resources, with visibility into the suppressed alerts associated with each affected device.
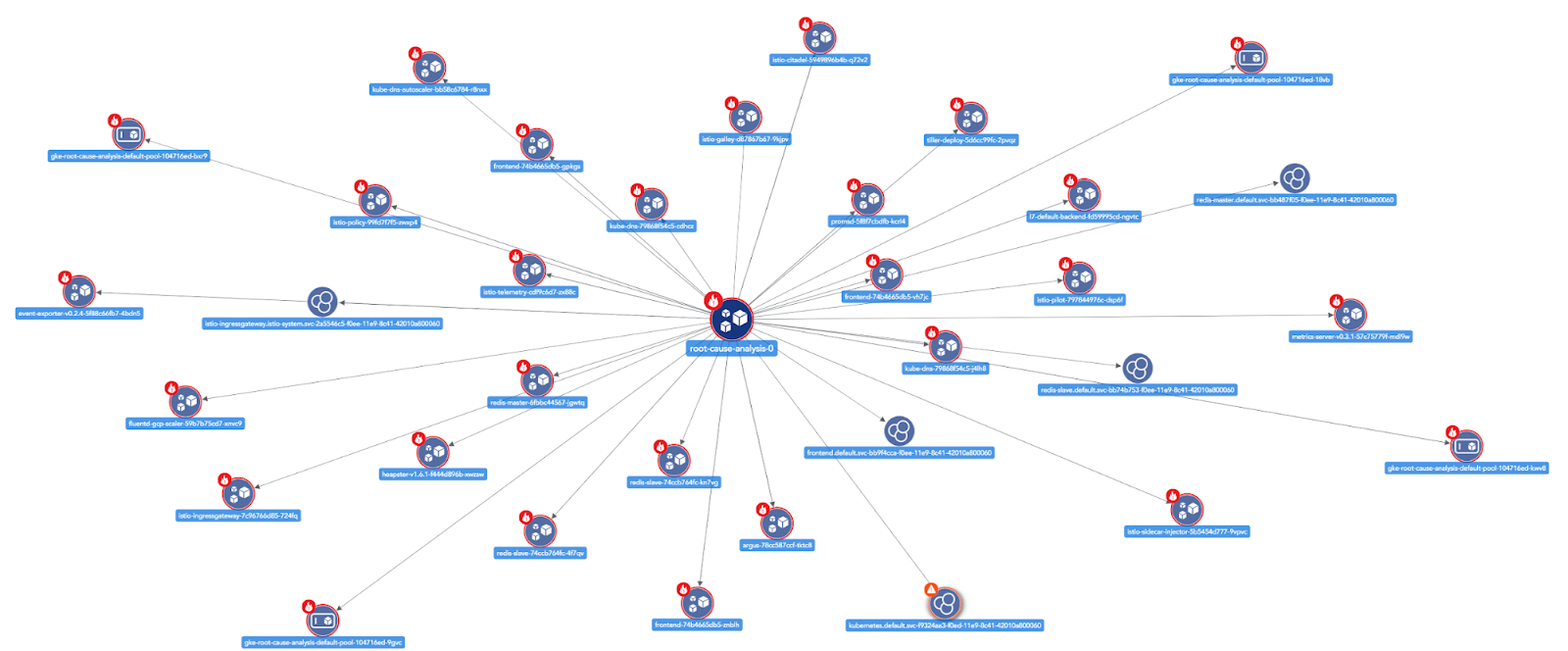
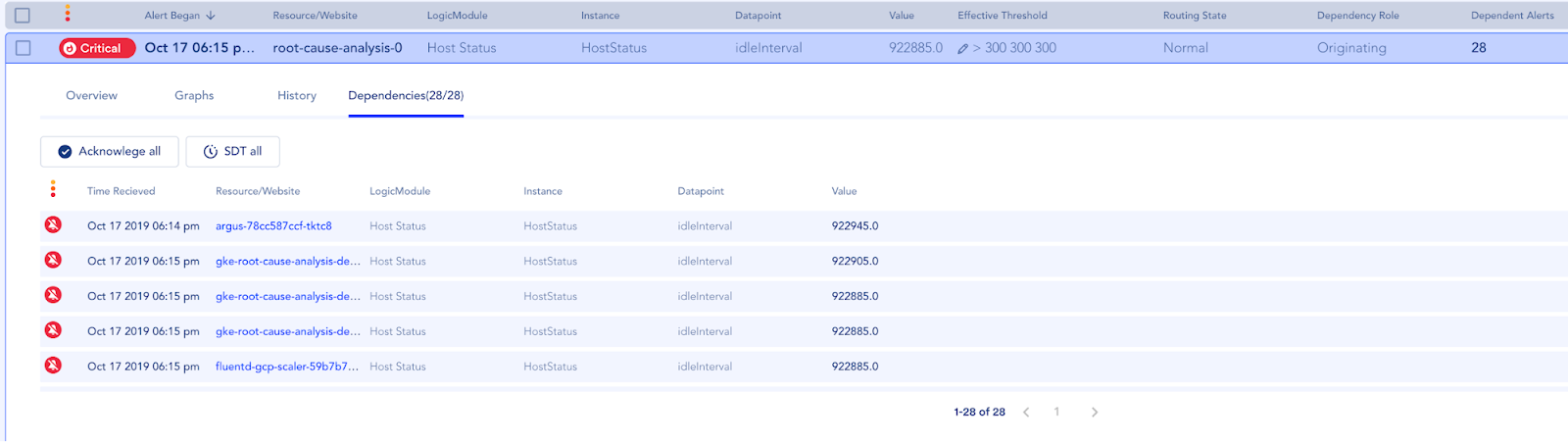
The originating cause alert is identified, dependent alerts are grouped and alert notifications for dependents are disabled:
Tech:
In this case, the machine learning technique most likely used is Dependency-based Root Cause Analysis (RCA), which involves analyzing relationships between resources to identify dependencies and the root cause of issues.
Specifically, a possible machine learning method used for this type of task is Graph-based Machine Learning or Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). These models are designed to handle data that can be represented as graphs, where the resources (e.g., network nodes, devices) are the nodes, and the relationships between them are the edges. GNNs can effectively analyze the network topology to determine which nodes (resources) are affected and which are the root causes of the issues, based on their dependencies.
Additionally, Supervised Learning techniques (e.g., classification models) could be used to predict which alerts are related to the root cause, based on historical data and known alert patterns, further enhancing the accuracy of the RCA process.